
Understanding “what does bookkeeper do” and the eight-step accounting cycle is crucial for entrepreneurs and managers who aim to improve their financial management skills. In a changing business environment characterized by innovation, adept bookkeeping plays a role. It serves as a catalyst that supports financial stability and drives operational excellence. This process involves maintaining records combined with economic analysis, which forms the basis for well-informed decisions, sustainable growth, and gaining a competitive edge in a dynamic market landscape.
Bookkeepers have a role in ensuring that the organization’s financial records are precise and current. Their task is to present an understandable overview of the organization’s well-being.
Data entry: Accurate data entry is a foundation for bookkeeping. Bookkeepers, known for their attention to detail make sure that every transaction, no matter how small or large, is recorded with precision. This meticulous approach forms the basis for all analyses, forecasts, and decision-making.
Bank reconciliation: Beyond recording transactions, bookkeepers also play a role in validation. They carefully compare their entries with bank statements to confirm the accuracy of each transaction. This reconciliation process is essential in identifying and correcting any discrepancies to maintain the integrity of statements.
Monthly reports: The culmination of validated transactions leads to the creation of reports. Bookkeepers synthesize the data into reports that provide insights into an organization’s financial position. These reports serve as tools, for stakeholders, empowering them with the information needed to make informed decisions.
Accounts Receivable: In the field of accounting it is crucial to manage receivables. Bookkeepers did not send out invoices. Also, keep an eye on them, ensuring that payments are made on time and maintaining a healthy cash flow.
Accounts Payable: The balancing act also involves managing payables. Bookkeepers make sure that every amount owed is properly accounted for, verified, and paid promptly. This helps build relationships with suppliers and ensures operational efficiency.
Payroll: Besides these responsibilities, bookkeepers dive into the world of payroll. They handle every calculation, deduction, and payment with precision to ensure that employees are accurately and promptly remunerated.
Tax Filing: One of the responsibilities is filing taxes. Accountants delve into the world of tax codes, rules, and compliance. They have the task of preparing, verifying, and submitting tax returns. Every detail, deduction, and credit is carefully examined to ensure accuracy and compliance. In a changing landscape of tax laws and regulations, accountants act as guides ensuring that businesses not only comply but also optimize their tax positions. They analyze data, apply tax codes, and diligently prepare returns that accurately reflect the financial position and obligations of the business.
End of Year Reporting: As the year comes to an end accountant’s role becomes more complex. They play a role in assisting with the creation of income statements and balance sheet reports. These comprehensive documents go beyond requirements; they are like mirrors reflecting the financial well-being, accomplishments, and challenges faced throughout the year. Accountants carefully consolidate data, make adjustments, and prepare reports that are both compliant with regulations and provide valuable insights. These reports serve as a foundation for planning, forecasting, and investor relations.
Business Strategy: In the world of business planning and decision-making, bookkeepers play a role as silent strategists. They provide insights through forecasts, budget analyses, and financial evaluations that shape business strategies. By examining trends assessing well-being and predicting future financial paths, bookkeepers arm business leaders with data-driven information. Their analyses go beyond numbers as they interpret this data to develop strategies, identify growth opportunities, and pinpoint areas for improvement.
Streamlining Business Processes: In this era of advancement, bookkeepers also contribute to innovation in business processes. They. Implement software solutions and internal controls to streamline operations and enhance performance. With their understanding of data, they can identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and opportunities for automation and optimization.
Knowledge Sharing: Another aspect of their role is sharing knowledge. Bookkeepers educate staff on practices in bookkeeping and the effective utilization of software solutions. They ensure that the team is equipped with the skills and knowledge to efficiently navigate the world of financial management.
Virtual Office Support: As the world continues its transformation journey, bookkeepers are also offering virtual office services. They are responsible for managing communication handling duties and ensuring that businesses maintain efficiency in a virtual setting.
Acting as a liaison: Bookkeepers often act as a connection between the company and external entities such as accountants and tax authorities. They ensure communication, accurate data sharing, and adherence to compliance requirements.
The accounting cycle is an 8-step process and serves as the backbone of bookkeeping duties. This process captures bookkeeping principles, ensuring that every step is carefully crafted to guarantee precise, transparent, and efficient financial reporting. Amid the age, this cycle seamlessly combines accounting practices with contemporary technological advancements, enabling businesses to stay adaptable, compliant, and well-informed.
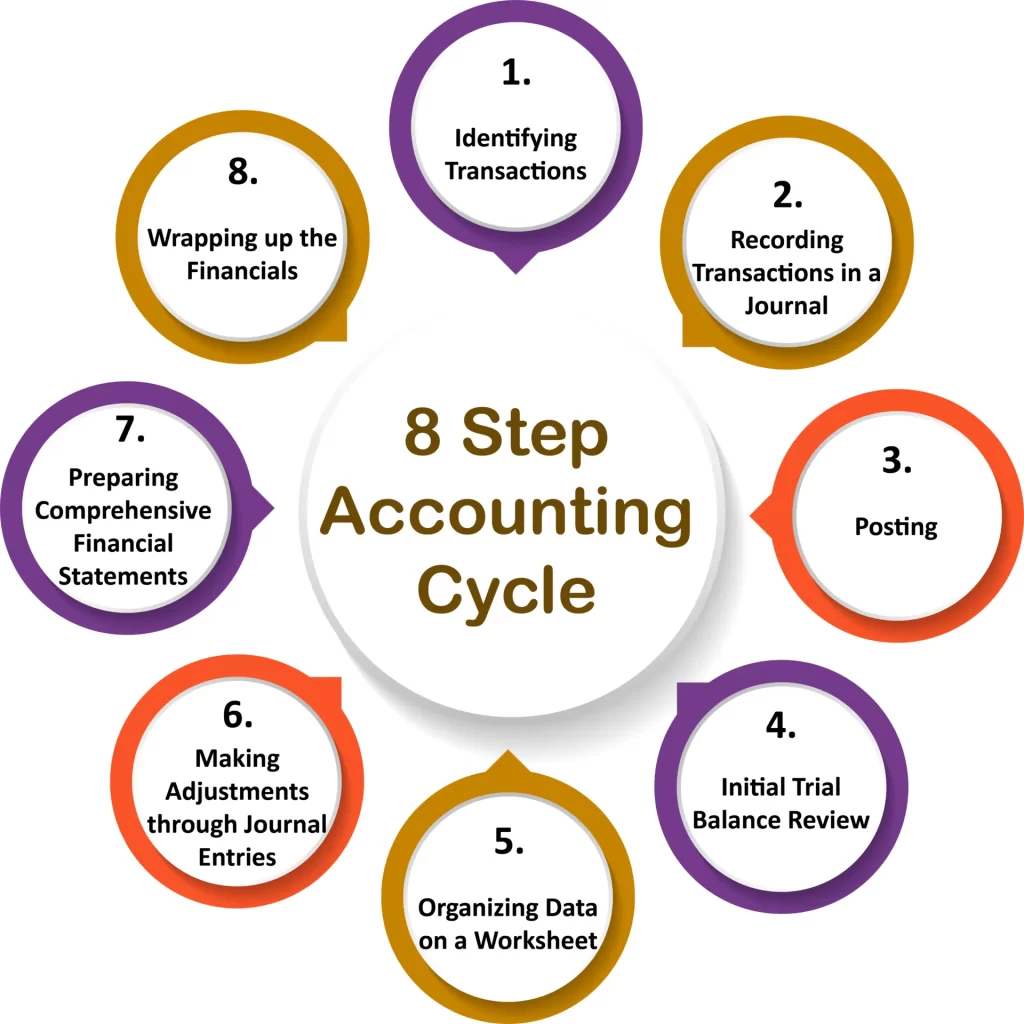
The accounting cycle begins by identifying every business activity with an impact. It’s not about recognizing these transactions but also validating them. This step is crucial for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of each transaction, which forms the foundation for stages. In a world where precision in finances is paramount, this initial phase leaves no room for compromise.
After identifying and validating the transactions, the next important step is to record them in a journal. This involves providing information about each transaction, capturing its essence and financial implications. The level of detail at this stage creates a log that plays a role in reviews, audits, and analysis. In today’s data era, every entry contributes to businesses’ analytical capabilities. Facilitates well-informed decision-making.
The phase involves transferring journal entries to ledger accounts. It’s a process of organization and categorization that ensures each transaction finds its place within the financial records. Ledger accounts serve as transaction repositories, which sets the stage for detailed analysis and reporting.
At this stage, we carefully. Verify the trial balance. It’s a process where we compare the debit and credit entries to ensure everything is balanced. This serves as a review, helping us identify any discrepancies that need to be addressed. The unadjusted trial balance we create here is the version that will undergo adjustments to accurately reflect the financial position of the business.
Next, we create a worksheet to organize and adjust data for our statements. This acts as a draft where we make adjustments to ensure accuracy, compliance, and a true reflection of our business’s health. This phase is crucial in laying the foundation for our statements.
During this phase, we make adjustments to account balances. Our goal is not accuracy but compliance with accounting standards and principles that apply to us. This refining process allows us to tune the trial balance with precision.
The final step involves preparing reports. After recording, adjustments, and verifications, these statements encapsulate the picture of our business’s financial performance and position.
These statements serve as a guiding light for stakeholders, investors, and management, providing insights influencing decision-making and shaping plans.
The process comes to an end with the completion of accounting tasks. Getting ready for the cycle. It’s a moment of closure and preparation for a start, ensuring that the business is always prepared and well-informed.
In this union of numbers and transactions, technology plays a role. Companies, depending on their size, complexity, and specific requirements, employ levels of automation. Accounting software has become the trusted companion of bookkeepers, providing automation, precision, and speed. However, the human touch and manual oversight remain invaluable. Bookkeepers intervene at stages, bringing in their judgment, expertise, and discernment. Each business adapts the 8-step cycle to fit its financial and compliance landscape. This customization showcases the beauty of bookkeeping. An integration of tradition and technology that ensures businesses are not only financially informed but also strategically empowered.
The accounting cycle, consisting of 8 steps, is more than a process as it serves as a tool. Within these steps, we find the guarantee of accuracy, compliance, and valuable insights. Every phase of this cycle, starting from transaction identification to book closure, showcases the fascinating realm of accounting. Here, numbers are not merely. Given significance and purpose.
The multifaceted layers of bookkeeping and the accounting cycle steps represent an assemblage of data, numbers, and financial statements. It is, like an orchestra where accuracy, adherence, and thoughtful analysis come together to support a financial environment for businesses. The responsibilities of a bookkeeper go beyond the tasks of entering data and reconciling accounts. In their hands, every number, transaction, and financial statement becomes a resource that fuels informed choices, risk monitoring, and strategic decision-making.
Every bookkeeper, financial report, and accounting cycle brings us closer, to a destination where financial precision, operational efficiency, and strategic growth come together. When you choose the right accounting and bookkeeping support ally, you embark on a journey where each step is meticulously taken, and every number has significance. Every financial report opens the door to insights, for sustainable growth.
We at Accounting Farm, transcend traditional services of bookkeeping. When it comes to selecting accounting software, it’s crucial to comprehend the connection between advancements and manual proficiency. We provide a customized approach that caters to the requirements of each CPA/Accounting firm, guaranteeing that your accounting process is more than just a routine obligation but rather a valuable strategic resource.
Explore the benefits of outsourcing and learn how our team can support your firm with a range of accounting services. From tax preparation and bookkeeping to financial statement audits and advisory services, we provide scalable solutions to meet your evolving needs.
Connect with us even faster by booking a meeting today at a time that works best for you.
Top Accounting Outsourcing Services For CPAs, Accounting, and Bookkeeping Firms.
Hello,
Thanks for visiting our website!
How can we help you?
Start the chat
WhatsApp us